Author: Ryo Nakamura on December 19, 2024 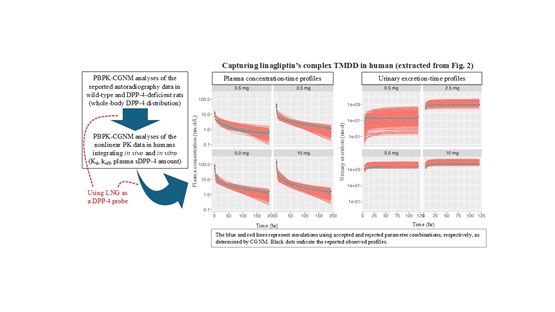
DPP-4 is an endopeptidase widely expressed in organs and tissues, regulating blood glucose by degrading incretin hormones. DPP-4 has two forms: transmembrane DPP-4 (tDPP-4), found on cell membranes, and soluble DPP-4 (sDPP-4), produced by the shedding of tDPP-4 into plasma. tDPP-4 predominates, especially on renal tubule brush borders. A previous PBPK model of the high-affinity DPP-4 inhibitor linagliptin (LNG) showed that considering target-mediated drug disposition (TMDD) by sDPP-4 and tDPP-4, along with DPP-4-mediated renal reabsorption, explained LNG's nonlinear plasma and urine pharmacokinetics. This suggests DPP-4's role in renal reabsorption and is consistent with the lack of nonlinear renal excretion in DPP-4 knockout mice. However, the complexities of parameter estimation, initial value selection, and integrating in vitro and in vivo data made it challenging to identify PBPK parameters fully explaining TMDD and nonlinear PK.
To address this, we used unique approaches in this study. First, we applied a cluster Gauss-Newton method (CGNM), assuming non-unique solutions to generate multiple initial value combinations for efficient parameter estimation. We also limited parameters based on in vitro data (e.g., DPP-4 expression and kinetics), clinical data, and incorporated a whole-body DPP-4 distribution pattern from autoradiography in DPP-4-deficient and wild-type rats into the human PBPK model. These additional methods helped refine processes and mechanisms to better estimate in vivo and in vitro phenomena.
In conclusion, using LNG as a DPP-4 probe and the PBPK-CGNM parameter estimation method, we clarified DPP-4's whole-body distribution in humans and its role in renal reabsorption. Beyond glycemic control, DPP-4 participates in biological functions, including inflammation and fibrosis in renal pathology. Since DPP-4 is highly expressed in the kidney, further elucidating DPP-4’s 'dynamic distribution' in vivo will provide insights into renal pathology and help identify new drug targets.

The comment feature is locked by administrator.